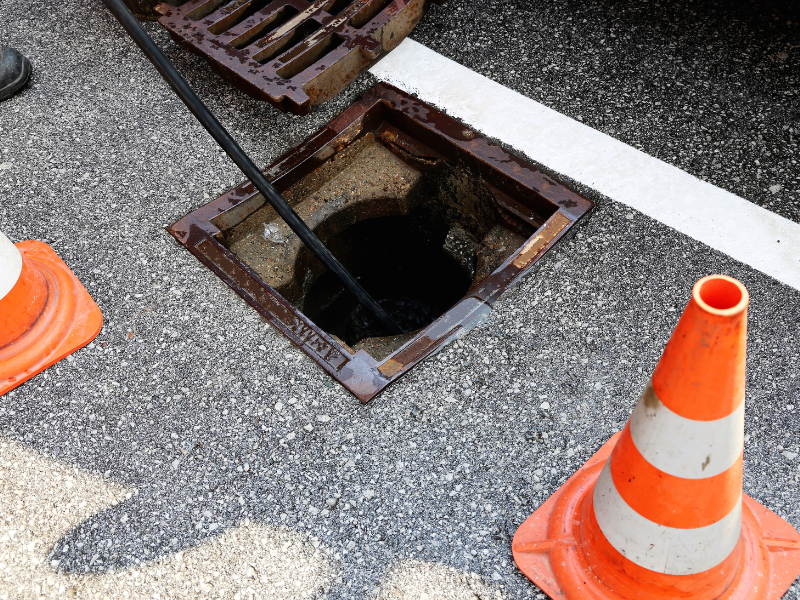
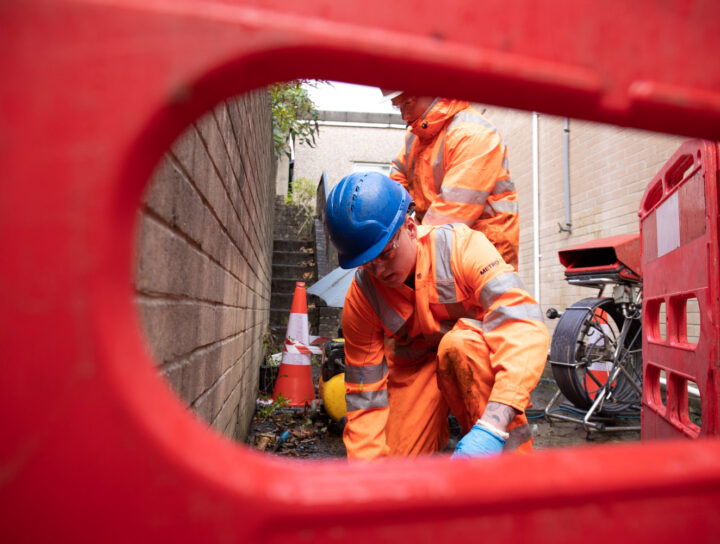
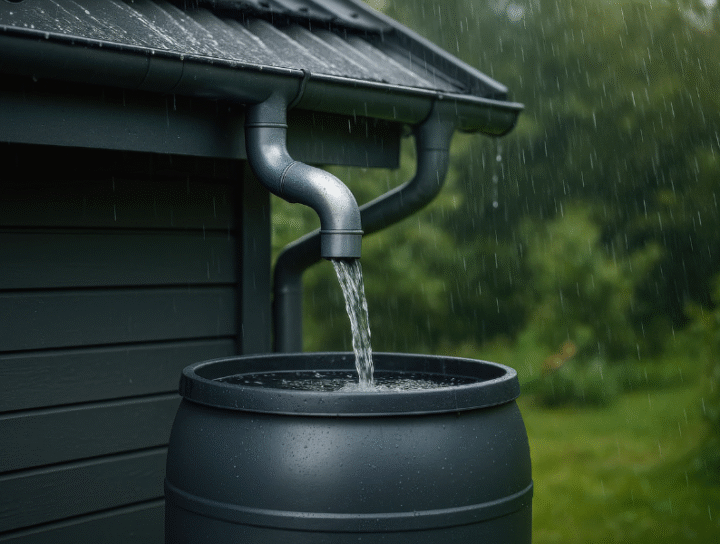
Gullies are an essential part of any property’s water management system. A gully is a drainage fitting with an open top, a designed base, and one or more side outlets. They connect wastewater, stormwater, or rainwater outlets to the appropriate drains and help drain surface water from areas prone to flooding.
Gullies fall into two main categories: road gullies and domestic gullies. While their primary function is to remove water, they also serve secondary purposes. Drain gullies help prevent unpleasant odours and stop rodents from entering or leaving the drainage system. Although they are designed to block leaves, twigs, and debris from causing issues, gullies are not immune to blockages themselves. Regular maintenance is essential to keep them functioning effectively.
Drain Gullies, Contents:
Where are Gullies Found?
Gullies are needed wherever there is a water discharge point(s) around the outside of the property to collect surplus run-off and direct it back into the foul water system. The most common places to find gullies include:
- Rainwater downpipes
- Patio areas
- Outside taps
- External discharge pipes (dishwasher, washing machines, etc)
With a combined drainage system, all wastewater, stormwater, and surface water are discharged into a single network and directed to one destination. This type of system is typically found in properties built before 1970.
Homes constructed after 1970 are more likely to have two separate drainage systems. Wastewater is directed to the main sewer system, while surface water and rainwater flow into a watercourse. This separation reduces pressure on the main system and prevents the mixing of clean and dirty water.
Although the purpose of gullies remains the same, their designs vary depending on location and specific requirements.
Drainage Gully Types
Road Drainage Gullies
Road drainage gullies are specifically designed to handle large volumes of surface water that accumulate on roads. Built to withstand the demands of heavy traffic environments, they are far more robust and efficient than domestic gullies, ensuring effective water management in these high-pressure areas.
Domestic Drainage Gullies
Domestic gullies are designed to channel surface water from gardens, rainwater, and wastewater from appliances like washing machines into the appropriate drains. They feature a grating or grid to block debris from entering the drainage system and include water traps to prevent unpleasant odours from resurfacing.
P–Trap Gully
A P-trap gully features a pipe shaped like the letter “P” and is commonly used to collect rainwater from a downspout. It connects to a grated drainage fitting known as a hopper. However, if a P-trap gully or its connecting drains become blocked, the design prevents the use of a drain rod to clear the obstruction.
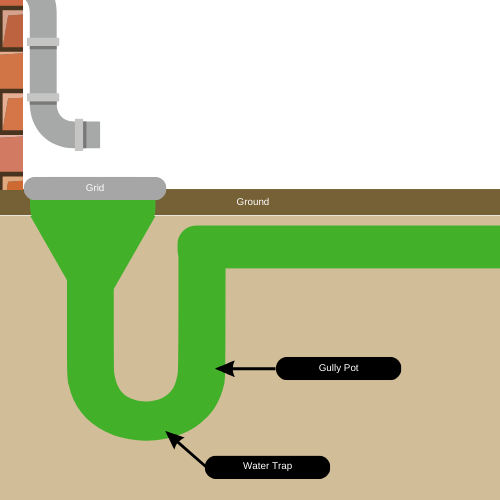
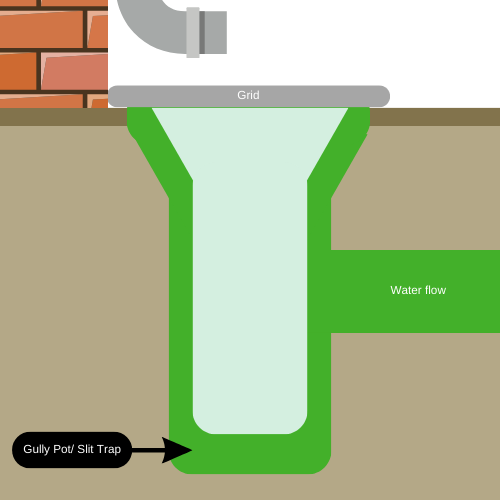
Bottle Trap Gully
Unlike the P-trap gully, the bottle gully eliminates the issue of tight bends that trap water. Instead, it uses a central chamber where water is forced up to reach the outlet pipe, leaving a space between the chamber and the gully wall. This design allows direct access to the outlet, making cleaning easier with its removable sleeve.
Prevention and Maintenance
Regular gully maintenance is essential to prevent blockages. Local councils are responsible for the maintenance of road gullies, while domestic gullies are the responsibility of property owners. Simple tasks like sweeping around gully grids and clearing out gutters can significantly reduce the chances of blockages.
To check your gully, inspect the grates for debris or signs of slow-draining water. Common causes of blockages include leaves, twigs, and other debris. If a blockage occurs, it’s important to act quickly to avoid flooding. Signs of a blocked gully include:
- Overflowing water
- Slow drainage
- Bad odours
Attempting to clear a gully without professional help risks pushing the blockage deeper into the drainage system or damaging the pipes. Metro Rod offers pre-planned maintenance services tailored to the needs of your property, ensuring your drainage system remains efficient and trouble-free.
FAQs
What is the difference between a gully and a ravine?
A gully is a man-made drainage fitting used to manage surface water, while a ravine is a natural feature formed by the erosion of soil and rock, often caused by water flow over time. Gullies are engineered for properties or infrastructure, whereas ravines are part of the natural landscape.
What’s the difference between a gully and a drain?
A gully is a drainage component that connects surface water or wastewater to underground drains, often using a grating to filter debris. A drain, on the other hand, is the pipework or system that transports water from properties to sewers or watercourses.
Do bottle gullies stop smelling?
Yes, bottle gullies help prevent odours by trapping water in their chamber, which creates a seal to block foul smells from escaping. Proper maintenance, such as clearing debris, is essential to keep them functioning effectively and prevent potential odours.
What is the difference between a gully and a trap?
A gully is a fitted structure designed to connect surface water or wastewater outlets to underground drains. A trap, such as a water trap in a gully, holds water to prevent unpleasant odours from rising through the drainage system.
Do gullies hold water?
A gully is a fitted structure designed to connect surface water or wastewater outlets to underground drains. A trap, such as a water trap in a gully, holds water to prevent unpleasant odours from rising through the drainage system.
Does a downpipe need a gully?
Yes, rainwater gullies are required for most downpipes to direct rainwater into the drainage system while filtering out debris such as leaves. This helps prevent blockages and manages water flow more efficiently.
What is the difference between a gully and a hopper?
A gully connects surface water or wastewater to the underground drainage system, while a hopper collects rainwater from various sources before directing it into a gully or other drainage infrastructure.
What are the disadvantages of gully traps?
Gully traps can sometimes become blocked by debris, requiring regular maintenance to stay effective. Additionally, certain designs, like P-trap gullies, may restrict access for unblocking with tools, making maintenance more challenging.

Talk to your local Metro Rod specialist
We are always happy to arrange a free site assessment and no obligation quotations for any work you might need. Alternatively, you can call our emergency hotline number on 0800 66 88 00
Get in touch Drainage Services


